When we announced Project Circe at this year’s ScyllaDB Summit we pledged to keep the community apprised of our progress every month. We’ll kick things off this month by covering the work we’ve done to make ScyllaDB an even-more-monstrous NoSQL database.
You can read about our long-term goals for Project Circe in our blog post from earlier this month. If you prefer to hear it directly, you can watch our CEO Dor Laor’s keynote from ScyllaDB Summit.
ScyllaDB Open Source 4.3
Along with all the other news at ScyllaDB Summit we released the latest version of our database, ScyllaDB Open Source release 4.3. This release makes our Change Data Capture (CDC) feature GA, and provides the foundation for our experimental feature for Alternator Streams — our DynamoDB Streams workalike. It also supports a unified installer, and a Google Cloud Platform (GCP) image. Specifically for Project Circe, this release removes the seed node concept in gossip; seed nodes are still used in the init process.
ScyllaDB Cloud on GCP
 We are now conducting a beta program to support ScyllaDB Cloud on GCP. This service brings our fully tested ScyllaDB Enterprise release to the GCP platform, where you will be able to run your Apache Cassandra or DynamoDB-compatible workloads. If you are interested in taking part of this early limited offering, please sign up for ScyllaDB Cloud.
We are now conducting a beta program to support ScyllaDB Cloud on GCP. This service brings our fully tested ScyllaDB Enterprise release to the GCP platform, where you will be able to run your Apache Cassandra or DynamoDB-compatible workloads. If you are interested in taking part of this early limited offering, please sign up for ScyllaDB Cloud.
ScyllaDB Operator
 We recently announced the General Availability (GA) release of ScyllaDB Operator, our production-ready open source project that allows users to manage their ScyllaDB clusters using Kubernetes (K8s).
We recently announced the General Availability (GA) release of ScyllaDB Operator, our production-ready open source project that allows users to manage their ScyllaDB clusters using Kubernetes (K8s).
To get started, watch the presentation on ScyllaDB Operator 1.0 on our ScyllaDB Summit on-demand site. Check out our ScyllaDB Operator page, where you can find links to download, read the documentation, and check out our free ScyllaDB University course to get you started.
WATCH SCYLLA OPERATOR 1.0 ON-DEMAND
New IO Scheduler
ScyllaDB 4.4-rc0 was created and one of its major premises is a better IO scheduler. The benefits of the new scheduler were covered at the summit Performance Enhancements session.
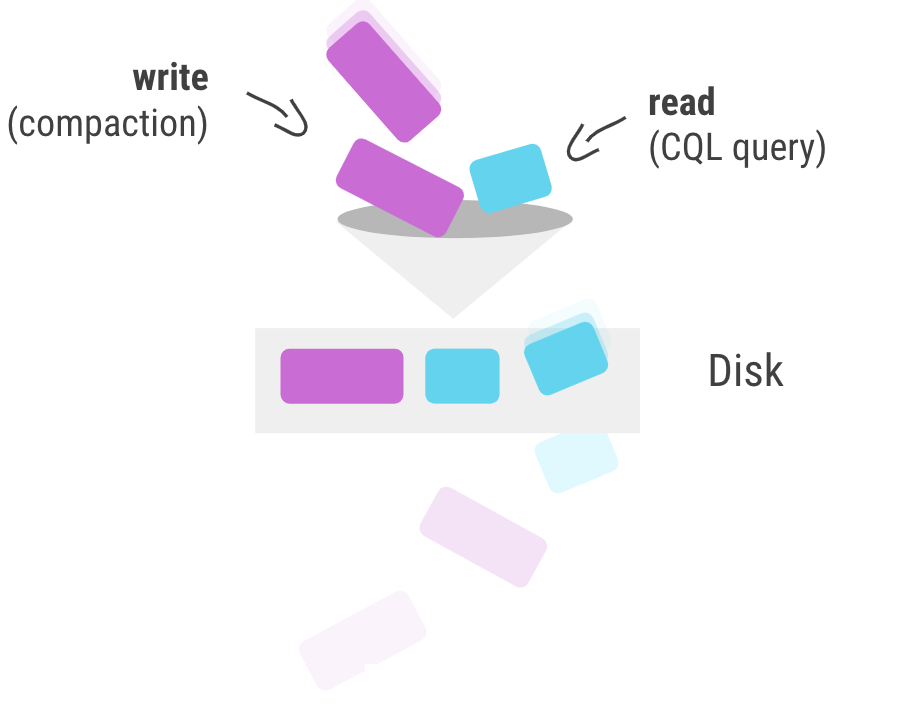
The new IO scheduler 2.0 has an active window that is large enough to saturate, but small enough to keep latency low.
The previous scheduler didn’t cope accurately enough with a mix of large IOs originating from blobs or compaction together with smaller, standard query IOs.
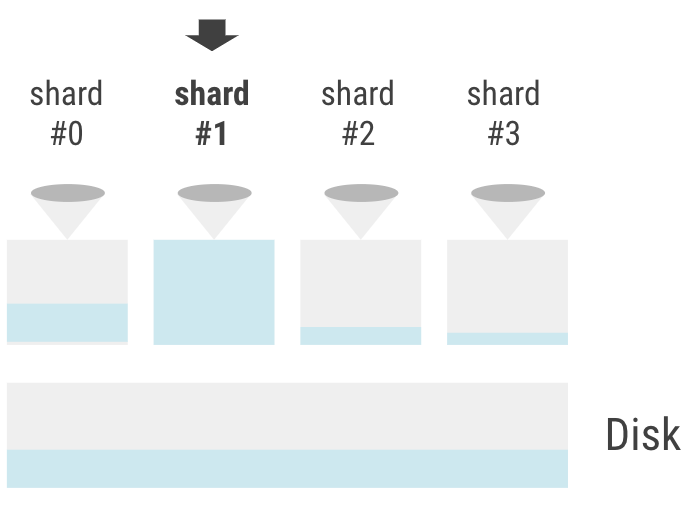
The original IO scheduler had unbalanced demand, and underutilized disk. Repairs and compactions ran at different times on different shards.
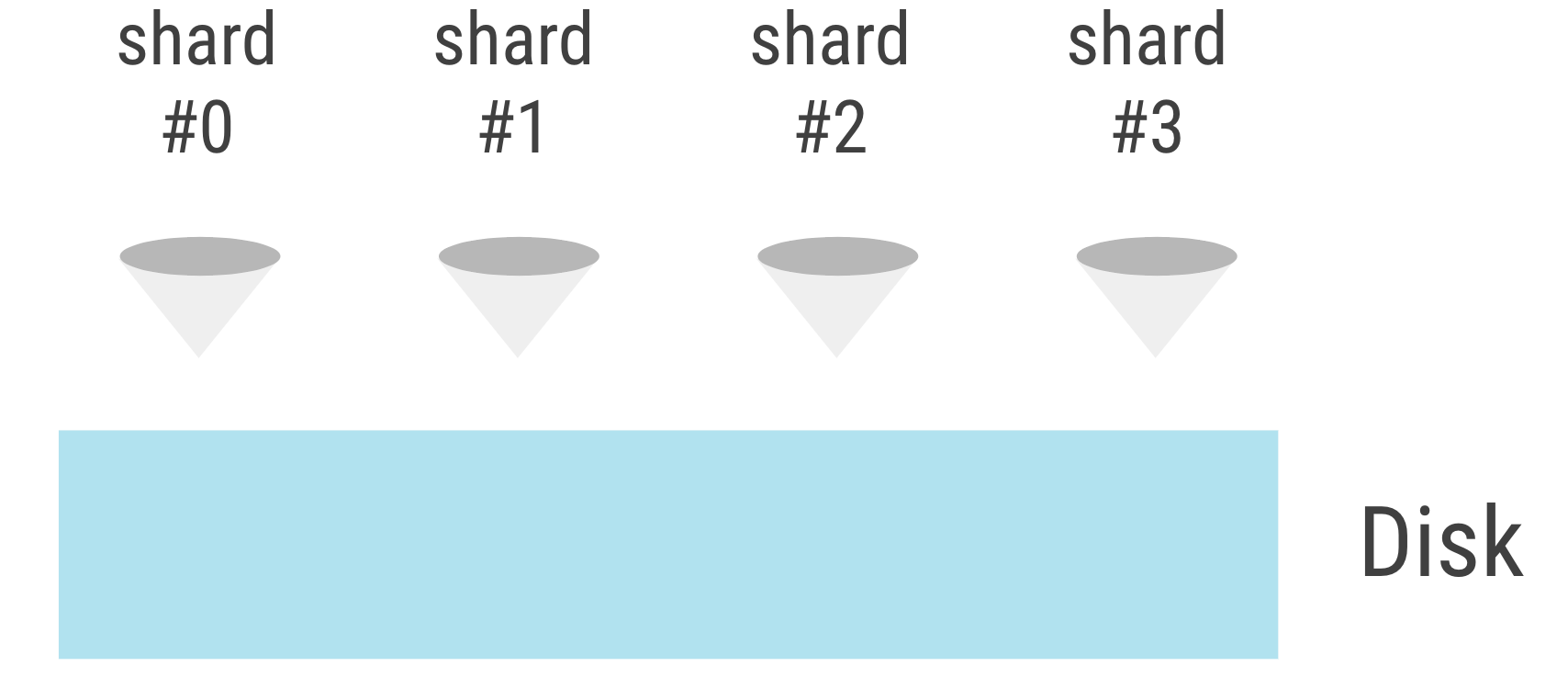
With the new IO scheduler 2.0, bandwidth and IOPS are shared;
each shard can use the whole disk.
The new scheduler shares bandwidth with all of the shards in the node, thus can borrow bandwidth and performs much better in environments with low IO bandwidth.
WATCH SCYLLA PERFORMANCE ENHANCEMENTS ON-DEMAND
Don’t Miss a Session!
These are just a few of the highlights from ScyllaDB Summit 2021. All of our sessions are available via our on-demand site, you can sign up to watch them all here:
WATCH ALL THE SCYLLA SUMMIT ON-DEMAND VIDEOS