Cassandra Clustering Key FAQs
What are clustering keys in Cassandra? Cassandra Primary Keys vs Clustering Keys vs Partition Keys?
Clustering keys in Cassandra are an essential component of the data model used to organize data within a partition. Apache Cassandra is a distributed NoSQL database known for high availability and managing large amounts of data. Clustering in Cassandra is a storage engine process that involves sorting and clustering columns and data based on the logical criteria of the model.
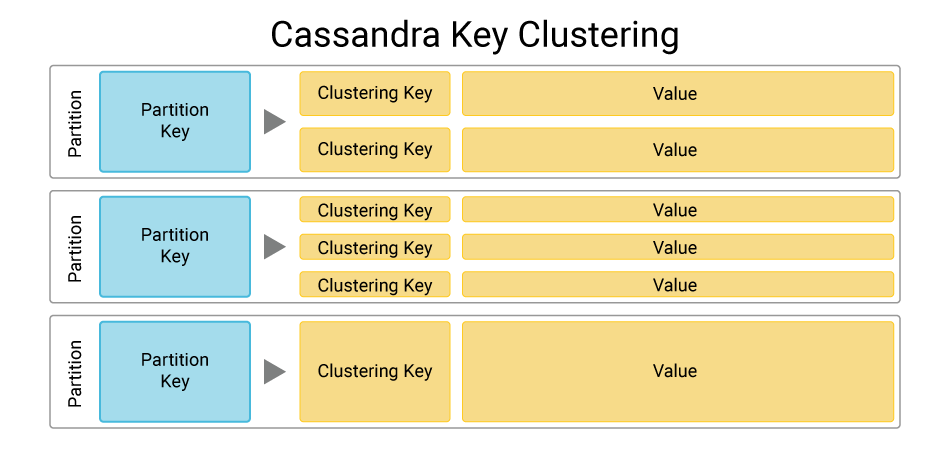
Partition key. The partition key is part of the primary key and defines which node will store the data based on its hash value and distributes data across the nodes in the Cassandra cluster. All rows with the same partition key will be stored together on the same node.
Clustering key(s). The clustering key(s) follow the partition key in the definition of the primary key in Cassandra. The clustering key sorts the data within a partition, allowing rows with the same partition key to be ordered based on their different clustering key values.
For example, a table may store information about books. The primary key might be a composite key of two parts: the partition key is the “genre,” such as mysteries or nonfiction, and the clustering key is “publication year.” This will ensure that mystery books are stored on one node based on the partition key, non-fiction books are stored on another, and that within each partition books will be ordered by their publication year based on the clustering key.
Cassandra primary key clustering is especially important when dealing with queries that retrieve data from a single partition since it allows efficient data retrieval in sorted order. It’s important to design the clustering key based on the types of queries that are expected to optimize data access patterns.
Although there can be more than one clustering key, there is no support for Cassandra multiple clustering keys within the primary key definition. In fact, the partition key is required to distribute data in the cluster, while the clustering key is optional.
Cassandra Primary Key vs Clustering Key
Cassandra primary key. The primary key is part of the primary key and a combination of one or more columns that uniquely identify a row in a Cassandra table. It consists of the partition key and the optional clustering key(s) and distributes data across nodes in the Cassandra cluster and determines which node will store the data for a particular row. Each row must have a unique combination of values for the partition key to ensure even data distribution across the cluster. The primary key is declared when the table is created and cannot be modified later.
Cassandra clustering key. The clustering key is a part of the primary key and is responsible for sorting the data within a partition. It defines physical data order within a partition and is used to retrieve data from a single partition key in sorted order. A table can have zero or more clustering keys, and if present, they come after the partition key in the primary key definition. The order of clustering columns within the primary key determines the order of data sorting within a partition. The clustering key is optional; if not specified, the rows within a partition are stored in the order they are inserted.
Cassandra Clustering Key vs Partition Key
There are a few key differences between Cassandra partition keys vs clustering keys that are important to highlight here:
Partition key differences. The partition key distributes data across nodes in the cluster and determines which node to store the data on for a particular row in the table for the Cassandra data model. In a Cassandra table, all rows with the same partition key will be stored together on the same node, forming a single partition. The choice of partition key is essential for even data distribution across the cluster to ensure scalability and avoid hotspots (nodes with disproportionately high data load). Well-designed Cassandra partition key clustering should spread data uniformly across nodes and support the desired query patterns.
Clustering key differences. The Cassandra partition key and clustering key serve different purposes in the Cassandra data model. The clustering key determines the physical order of data within a partition and is essential for performing range queries or retrieving data in sorted order based on specific criteria. Rows within a partition are organized and sorted based on the values of the clustering key(s). A table can have zero or multiple clustering keys. If no clustering key is specified, the data within a partition will be stored in the order they were inserted.
The Cassandra partition and clustering keys have different functions, but very generally, the partition key distributes data distribution across the cluster, determining data storage issues, and ensures scalability, while the clustering key sorts data, defines the order, and facilitates efficient queries and data retrieval.
Cassandra Data Modeling
Cassandra data modeling involves designing data structure and organization to achieve efficient and effective data storage and retrieval in Apache Cassandra’s distributed environment. Proper data modeling is crucial for achieving optimal, balanced results.
Selection of primary key columns is a critical piece of ensuring optimal Cassandra clustering key performance. The partition key distributes data across the cluster and should be chosen carefully to ensure distribution is even. An unsuitable partition key can lead to hotspots, where certain nodes in the cluster become overloaded with data, while others remain underutilized.
Cassandra clustering key order is responsible for sorting data within a partition. Cassandra query by clustering key is useful when querying data in a specific order is one of the goals.
Cassandra’s data modeling heavily revolves around choosing appropriate partition keys and clustering keys based on the access patterns and query requirements of your application. The goal is a balance between even, scalable data distribution and query performance and data retrieval needs that results in an efficient, functional, scalable data model.
Understanding query patterns is central to data modeling in Cassandra, which heavily depends on the queries the user intends to execute. Modeling should be optimized for the types of queries expected to be run on the data. Pre-aggregating or duplicating data in specific tables can help improve query performance.
Data replication and consistency across multiple nodes helps ensure high availability and fault tolerance. Appropriate replication factors and consistency levels can balance data durability, consistency, and performance of reads and writes.
What is the difference between a partition key, a composite key, and a clustering key in this context? A Cassandra composite clustering key is a primary key that consists of multiple columns, allowing for the creation of a more complex and flexible key structure.
A composite key is formed by combining two or more columns to uniquely identify each row in a table. The composite key can be composed of both a partition key and clustering key(s).
The partition key is the first part of the composite key that distributes data across nodes in the cluster. All rows with the same partition key value will be stored together on the same node. The partition key’s values must be unique within the dataset to ensure even data distribution.
In the context of the composite key, clustering key(s) are the subsequent pieces responsible for sorting data within a partition and specifying the physical order of data storage. The clustering order of columns within the composite key definition dictates the sort order within the partition.
Composite keys allow for more flexibility in data modeling, as they enable the design of tables with complex primary keys that cater to various query patterns and access requirements. By combining multiple columns in a composite key, more sophisticated data retrieval scenarios, such as range queries, descending order/sort order, and filtering based on multiple criteria, can be supported.
Developers use Cassandra Query Language (CQL) to create and manage the schema of Cassandra tables, including their structure, column names, data types, and primary key definition. The primary key is specified using CQL during table creation.
CQL allows developers to create tables, insert new data into them, and provides a flexible querying mechanism for interaction in Cassandra tables. CQL also allows for data updates and deletions using the UPDATE and DELETE statements, and provides the option to set the consistency level for each query, determining the level of data consistency required for read and write operations. Setting the appropriate consistency level is essential for maintaining data integrity in distributed environments.
Does ScyllaDB Support Cassandra Clustering Keys?
Yes. API-compatible with Apache Cassandra, ScyllaDB is a modern high-performance NoSQL database that supports core Cassandra data models, with the benefit of increased performance (predictable low latencies) from deep architectural advancements that reduce costs, maintenance, and overhead vs Cassandra.
Years after its revolutionary debut and broad adoption, many companies have recognized the many underlying limitations of Cassandra. Leading companies such as Comcast, Discord, Expedia, Fanatics, Samsung, and Rakuten use ScyllaDB’s “monstrously fast and scalable” database — fully compatible with Cassandra, but without the architectural downsides of Apache Cassandra or the costs of databases like Amazon DynamoDB.
Learn more here.