Frank Ober of Intel joined me for a quick interview on what he will be presenting at ScyllaDB Summit 2017. Frank, like many other speakers attending the Summit, is an expert in his field and will present their experiences and knowledge of the industry. Let’s begin the interview and learn more about what Frank will be presenting at the Summit.
Please tell us about yourself and what you do at Intel?
I am a Data Center Solutions Architect in the Non-Volatile Memory Group of Intel and like to delve into use cases for the emerging memory hierarchy after a 25-year Enterprise Applications IT career. I regularly test and benchmark Intel SSDs primarily with database workloads and am responsible for many technology proof point partnerships.
How did you get started as a Solutions Architect?
I was an IT developer and systems performance architect for many years, 20+ in fact. Then I heard about the non-volatile memory revolution that Intel was pursuing and how big that was. It was a huge bet on non-volatile memory that could rival DRAM and I was “all in” and I haven’t looked back since.
What will you be talking about at ScyllaDB Summit 2017?
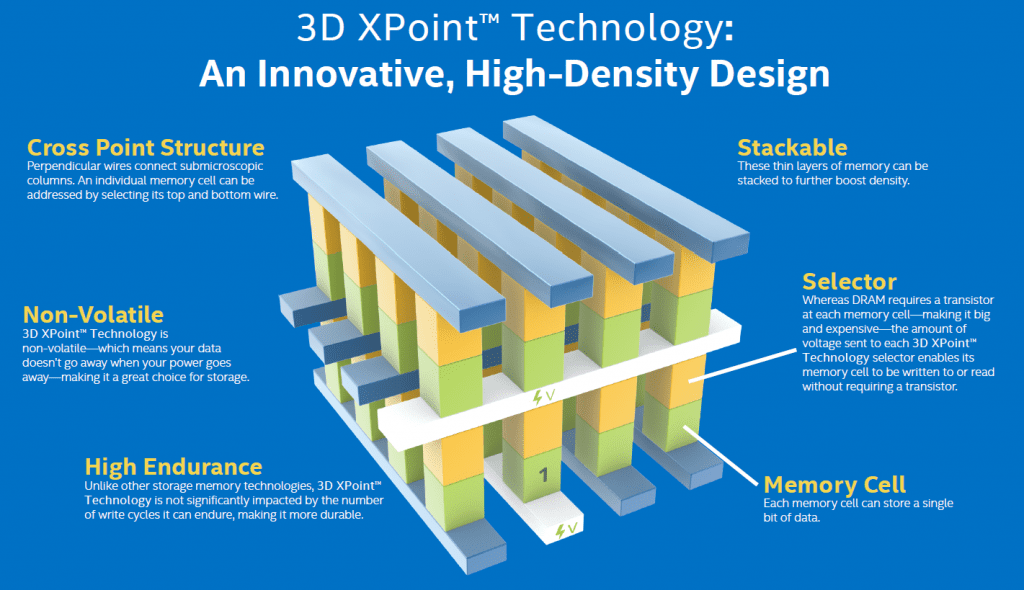
How NVMe has evolved with the 3D XPoint media into the Intel Optane Technology and what this family of products brings to just standard SSDs. Also, how you can look at Optane as a differentiator to SSDs, the best use cases, data and examples from the Open Source world, and a short demo of DirectIO features that are coming to Java 9 and 10.
How is Optane a differentiator to SSDs?
SSDs are great. However, Optane is much better because it is balanced and built for high random write workloads. The star of the show is the 3D XPoint memory which is designed more for memory access than bigger block storage. With that magical memory design, you get faster access (sub 10 microsecond at 4kb), and the ability to do things like synchronous IO which was never usable on HDD in high-performance designs. Random write performance on Optane can never be touched by NAND and certainly not HDDs because NAND must be queued heavily to perform and Optane doesn’t need that and maintains the best performance at low queue depths. That’s why we call it the world’s most responsive SSD.
How can databases take advantage of Optane?
Less DRAM more Optane. The database has always loved DRAM to buffer or cache its data. Now, there is another tier of memory which is the first new memory to hit the market in about 25 years. Use it, change your DRAM ratios, lower them, use Optane with DirectIO reads, and see how Optane can keep your service levels high and provide you flexibility at lower cost. ScyllaDB has this better architecture ready today!
What types of users can take advantage of Optane?
The innovators and early adopters of course. We have a customer that wants to take the colder objects of his CDN out of DRAM and onto bigger and cheaper Optane and use DirectIO so it is a direct cache to the user. We are finding database companies like ScyllaDB realizing that less DRAM doesn’t mean less acceptable performance. With Optane and ScyllaDB, you can take advantage of persistency in the architecture. Best of all, bigger capacities gives you that ability to use more data for your VM density or database driven decision making.
What type of audience will be interested in your talk?
Any developer or systems engineer up through technology-oriented decision makers focusing on improving their I/O with better SSDs.
Where can we learn more information about your talk?
To learn more about Optane, please visit the main site.
Thank you very much, Frank. We can not wait to see your talk in person and learn more.
ScyllaDB Summit is taking place in San Francisco, CA on October 24-25. Check out the current agenda on our website to learn about the rest of the talks—including technical talks from the ScyllaDB team, the ScyllaDB roadmap, and a hands-on workshop where you’ll learn how to get the most out of your ScyllaDB cluster.





